Introduction
In today’s fast-paced world, having reliable and efficient power cables is crucial for both residential and commercial applications. But how do you choose the right one? Let’s dive into the world of power cables and explore what you need to know before making a purchase. Imagine your electrical system as the veins and arteries of your home or business; power cables are the lifeblood that keeps everything running smoothly. Whether you’re setting up a new office, renovating your home, or maintaining industrial equipment, understanding the intricacies of power cables can save you time, money, and a lot of headaches.
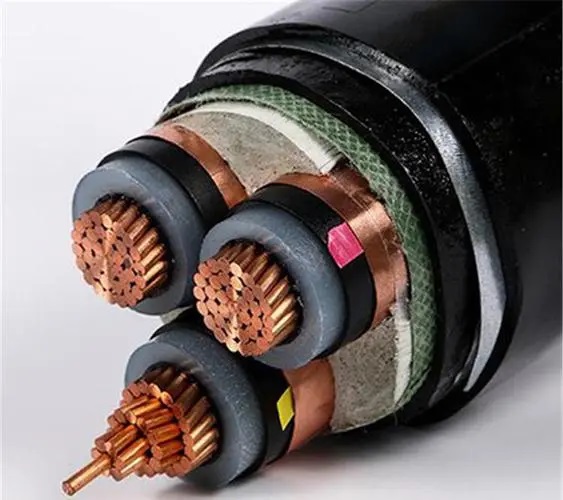

Understanding Power Cables
So, what exactly are power cables? Essentially, they are electrical cables used to transmit electrical power. They come in various types, each designed for specific applications. From powering household appliances to industrial machinery, these cables play an indispensable role in our daily lives. Think about it: without power cables, we wouldn’t have the luxury of flipping a switch to turn on the lights, charging our smartphones, or even running essential medical equipment.
Power cables are composed of conductors, insulation, and sometimes additional protective layers. The conductor is usually made of copper or aluminum and is responsible for carrying the electrical current. The insulation surrounds the conductor and prevents electrical leakage, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Types of Power Cables
When it comes to power cables, there are three main categories: low voltage, medium voltage, and high voltage.
Low Voltage Power Cables
Low voltage cables are typically used for household appliances and lighting. They handle voltages up to 1kV and are perfect for everyday electrical needs. These cables are commonly found in residential wiring systems, small businesses, and light commercial applications. They are designed to be flexible and easy to install, making them ideal for a wide range of uses.
For example, when you plug in your toaster or microwave, you’re relying on low voltage power cables to safely deliver the electricity needed to operate these appliances. These cables are also used in home entertainment systems, computer networks, and security systems.
Medium Voltage Power Cables
Medium voltage cables are used in industrial settings where higher power levels are required but not extreme voltages. These cables usually handle voltages between 1kV and 35kV. They are commonly used in manufacturing plants, refineries, and other industrial environments where machinery and equipment require more power than what low voltage cables can provide.
Medium voltage cables are built to withstand harsher conditions compared to their low voltage counterparts. They often feature additional layers of insulation and protective coatings to resist chemicals, moisture, and physical wear and tear.
High Voltage Power Cables
High voltage cables are essential for transmitting electricity over long distances, such as from power plants to urban areas. They handle voltages above 35kV and are designed to withstand extreme conditions. These cables are critical for the backbone of our electrical infrastructure, ensuring that large amounts of electricity can be transported efficiently from generation sites to substations and distribution networks.
High voltage power cables are engineered with robust materials and advanced manufacturing techniques to ensure they can handle the immense electrical loads without breaking down. They often include multiple layers of insulation, shielding, and armoring to protect against environmental factors like temperature fluctuations, electromagnetic interference, and mechanical damage.
Materials Used in Power Cables
The two most common materials used for conductors in power cables are copper and aluminum. Each material has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications.
Copper Conductors
Copper is known for its excellent conductivity and flexibility, making it a popular choice for many applications. Its high conductivity means that less copper is needed to carry the same amount of current compared to aluminum, which can result in smaller and lighter cables.
Copper is also highly resistant to corrosion, which adds to its longevity and reliability. This makes it an ideal choice for environments where durability is crucial. For instance, in residential wiring systems where space is limited and flexibility is needed, copper conductors provide an efficient and reliable solution.
Aluminum Conductors
Aluminum is lighter and more cost-effective than copper but offers slightly lower conductivity. This makes it a suitable choice for applications where weight and cost are significant considerations. Aluminum conductors are commonly used in overhead power lines, where the reduced weight helps minimize structural support requirements.
However, aluminum is more prone to oxidation and requires additional protective measures to prevent corrosion. Despite this drawback, advancements in technology have led to the development of aluminum alloys that offer improved performance and durability.
Insulation Materials
The insulation materials also vary, with options like PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene), and rubber offering different levels of protection and flexibility.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is one of the most commonly used insulation materials due to its affordability and versatility. It offers good electrical insulation properties and is resistant to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. PVC-insulated cables are widely used in residential wiring systems, automotive applications, and low voltage power distribution.
XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene)
XLPE is known for its excellent thermal properties and high resistance to electrical stress. It can withstand higher temperatures compared to PVC, making it suitable for medium and high voltage applications. XLPE-insulated cables are often used in industrial settings where reliability and performance are critical.
Rubber Insulation
Rubber insulation provides exceptional flexibility and resilience in harsh environments. It is commonly used in applications where cables need to withstand physical stress, vibration, and exposure to extreme temperatures. Rubber-insulated cables are often found in mining operations, marine environments, and heavy-duty industrial machinery.
How to Choose the Right Power Cable
Choosing the right power cable involves several considerations. It’s not just about picking any cable off the shelf; you need to ensure that it meets your specific requirements for safety, performance, and longevity.
Determining Your Power Needs
First, you need to determine your power requirements. Are you powering a small appliance or an entire building? The amount of power needed will dictate the type of cable you should use. For example:
- For household appliances like refrigerators or washing machines, low voltage cables with sufficient current-carrying capacity will suffice.
- For industrial machinery or large HVAC systems, medium voltage cables might be necessary.
- For long-distance power transmission or high-power applications like substations, high voltage cables will be required.
Considering Environmental Factors
Next, consider the environmental factors such as temperature and exposure to chemicals or moisture. The environment where the cable will be installed plays a significant role in determining the appropriate insulation material and protective measures needed.
- If the cable will be exposed to outdoor elements or buried underground, it should have robust insulation and protective coatings to resist moisture and physical damage.
- In environments with high temperatures or chemical exposure, specialized insulation materials like XLPE or rubber may be necessary to ensure long-term reliability.
Checking Compliance with Standards
Lastly, ensure that the cable complies with relevant standards and regulations to guarantee safety and performance. Look for certifications from recognized organizations like UL (Underwriters Laboratories), IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), or ANSI (American National Standards Institute). These certifications indicate that the cable has undergone rigorous testing and meets industry standards for quality and safety.
Power Cable Specifications
Understanding the specifications of power cables is essential for making an informed choice. Each specification serves as a critical factor in determining the cable’s suitability for a particular application.
Gauge and Length
The gauge of the cable indicates its thickness and capacity to carry current. Thicker cables (with a lower gauge number) can carry more current, which is crucial for high-power applications. Conversely, thinner cables (with a higher gauge number) are suitable for lower power requirements.
The length of the cable affects its resistance and efficiency. Longer cables have higher resistance, which can lead to voltage drops and energy loss. It’s essential to choose the correct length to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. For example:
- Short cables (less than 50 feet) are ideal for indoor wiring and small-scale applications.
- Medium-length cables (50 to 200 feet) are suitable for outdoor installations and moderate power transmission.
- Long cables (over 200 feet) are necessary for extensive power distribution networks and industrial settings.
Voltage Rating
Voltage rating determines the maximum voltage the cable can handle without breaking down. Choosing a cable with an appropriate voltage rating is crucial to ensure safety and prevent electrical failures. Voltage ratings are typically categorized as:
- Low Voltage (up to 1kV): Suitable for household appliances, lighting, and small electronics.
- Medium Voltage (1kV to 35kV): Used in industrial machinery, manufacturing plants, and commercial buildings.
- High Voltage (above 35kV): Essential for long-distance power transmission, substations, and large-scale electrical infrastructure.
Temperature Rating
Temperature rating indicates the range of temperatures the cable can withstand safely. This specification is vital for applications exposed to extreme temperatures or fluctuating environmental conditions. For instance:
- Standard temperature ratings (up to 75°C) are adequate for most indoor residential and commercial applications.
- High-temperature ratings (75°C to 125°C) are necessary for industrial environments, outdoor installations, and areas with significant heat exposure.
- Specialized temperature ratings (above 125°C) are used in extreme conditions, such as mining operations, steel mills, and high-power transmission lines.
Benefits of Quality Power Cables
Investing in high-quality power cables comes with numerous benefits that extend beyond just functionality. Here are some key advantages:
Enhanced Safety
Quality power cables enhance safety by reducing the risk of electrical fires, short circuits, and other hazards. They are manufactured to meet stringent safety standards and include features like flame retardant insulation, moisture resistance, and robust protective coatings. This ensures that the cables can handle unexpected electrical surges and environmental stresses without compromising safety.
Improved Efficiency
Quality cables improve efficiency by minimizing energy loss during transmission. High-grade materials like copper or advanced aluminum alloys offer superior conductivity, reducing resistance and energy wastage. This results in more efficient power delivery, lower energy costs, and better overall performance of electrical systems.
Longevity and Durability
Additionally, quality power cables offer greater longevity and durability, saving you money on replacements in the long run. They are designed to withstand physical wear and tear, environmental factors, and mechanical stress. This means fewer maintenance issues, reduced downtime, and longer service life for your electrical infrastructure.
Where to Buy Power Cables
You can purchase power cables from various sources, each offering its own set of advantages and considerations.
Online Retailers
Online platforms often offer a wider selection and competitive prices. Websites like Amazon, eBay, and specialized electrical supply stores provide a vast range of options from different manufacturers. The convenience of online shopping allows you to compare products, read customer reviews, and make informed decisions from the comfort of your home.
However, it’s essential to ensure that you buy from reputable sellers with positive reviews and transparent return policies. Look for certifications and product descriptions that provide detailed specifications to avoid purchasing substandard or counterfeit products.
Physical Stores
Physical stores allow you to inspect the product before buying. Visiting local hardware stores, electrical supply shops, or specialized retailers lets you see the cables firsthand, ask questions to knowledgeable staff, and get personalized recommendations based on your needs.
While physical stores may have a more limited selection compared to online platforms, the ability to physically examine the product can provide peace of mind. Additionally, local stores often offer immediate availability, eliminating shipping times and potential delays.
Tips for Finding Reliable Sellers
Whether you choose to buy online or from a physical store, here are some tips for finding reliable sellers:
- Check for certifications: Ensure that the seller offers products that comply with industry standards and certifications like UL, IEC, or ANSI.
- Read reviews: Look for customer feedback and reviews to gauge the quality of the products and the reliability of the seller.
- Compare prices: While it’s tempting to go for the cheapest option, consider the overall value, including warranty, return policy, and customer support.
- Ask for recommendations: Consult with professionals or industry experts who can provide insights into reputable brands and sellers.
Maintenance and Care for Power Cables
Proper maintenance can extend the life of your power cables significantly. Here are some best practices for keeping your cables in top condition:
Regular Inspection Tips
Regularly inspect them for signs of wear or damage, such as fraying or exposed wires. Pay attention to areas where cables are bent or subjected to physical stress. Look for discoloration, cracks in the insulation, or any unusual odors that might indicate overheating or chemical exposure.
Conducting routine inspections helps identify potential issues early on, allowing you to address them before they escalate into more significant problems.
Proper Storage Practices
Store them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or moisture. Proper storage prevents degradation of insulation materials and reduces the risk of damage from environmental factors. If possible, use cable reels or spools to keep cables organized and prevent tangling.
Avoid storing heavy objects on top of cables or placing them in areas with high foot traffic where they might be accidentally damaged.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter any issues, troubleshoot promptly or consult a professional to avoid potential hazards. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- Overheating: If a cable feels excessively hot to the touch, it might be overloaded or have poor ventilation. Ensure that the cable is rated for the current load it’s carrying and improve airflow around it.
- Physical Damage: If you notice cuts, abrasions, or exposed conductors, replace the damaged section immediately. Temporary fixes like electrical tape may not provide adequate protection.
- Corrosion: For aluminum conductors prone to oxidation, use anti-oxidant compounds during installation and regularly check for signs of corrosion.
- Loose Connections: Ensure that all connections are secure and free from corrosion. Loose connections can lead to increased resistance and overheating.
Conclusion
To sum up, choosing the right power cable involves understanding your needs, considering various factors, and ensuring compliance with standards. By investing in quality power cables and maintaining them properly, you can enjoy enhanced safety, efficiency, and durability. So go ahead, make an informed choice and keep your electrical systems running smoothly!
Remember that your electrical infrastructure is only as strong as its weakest link. By paying attention to the details outlined in this guide—from selecting the right type of cable to ensuring proper maintenance—you can build a robust system that meets your power needs reliably and safely.
Post time: 2024-09-18
